Understanding the Benefits of Using Helium for Industrial Applications
Introduction to Helium in Industrial Applications
Helium, a colorless and odorless gas, is the second most abundant element in the universe. Known for its low density and inert nature, helium is increasingly finding its way into various industrial applications. Its unique properties make it indispensable for many processes, offering solutions that other gases simply cannot match.
From electronics manufacturing to medical technology, the utility of helium spans numerous sectors. As industries continue to evolve, understanding the benefits of using helium can lead to more efficient and innovative practices.

Unique Properties of Helium
Helium boasts several unique properties that make it ideal for industrial use. It is the lightest noble gas and remains non-reactive under most conditions. This inertness ensures that helium does not form compounds or react with other substances, making it incredibly safe for sensitive environments.
Additionally, helium has a remarkably low boiling point, which allows it to function effectively as a coolant in situations where extreme cold is required. Its high thermal conductivity further enhances its cooling capabilities, making it a preferred choice in cryogenics.

Applications in Electronics and Manufacturing
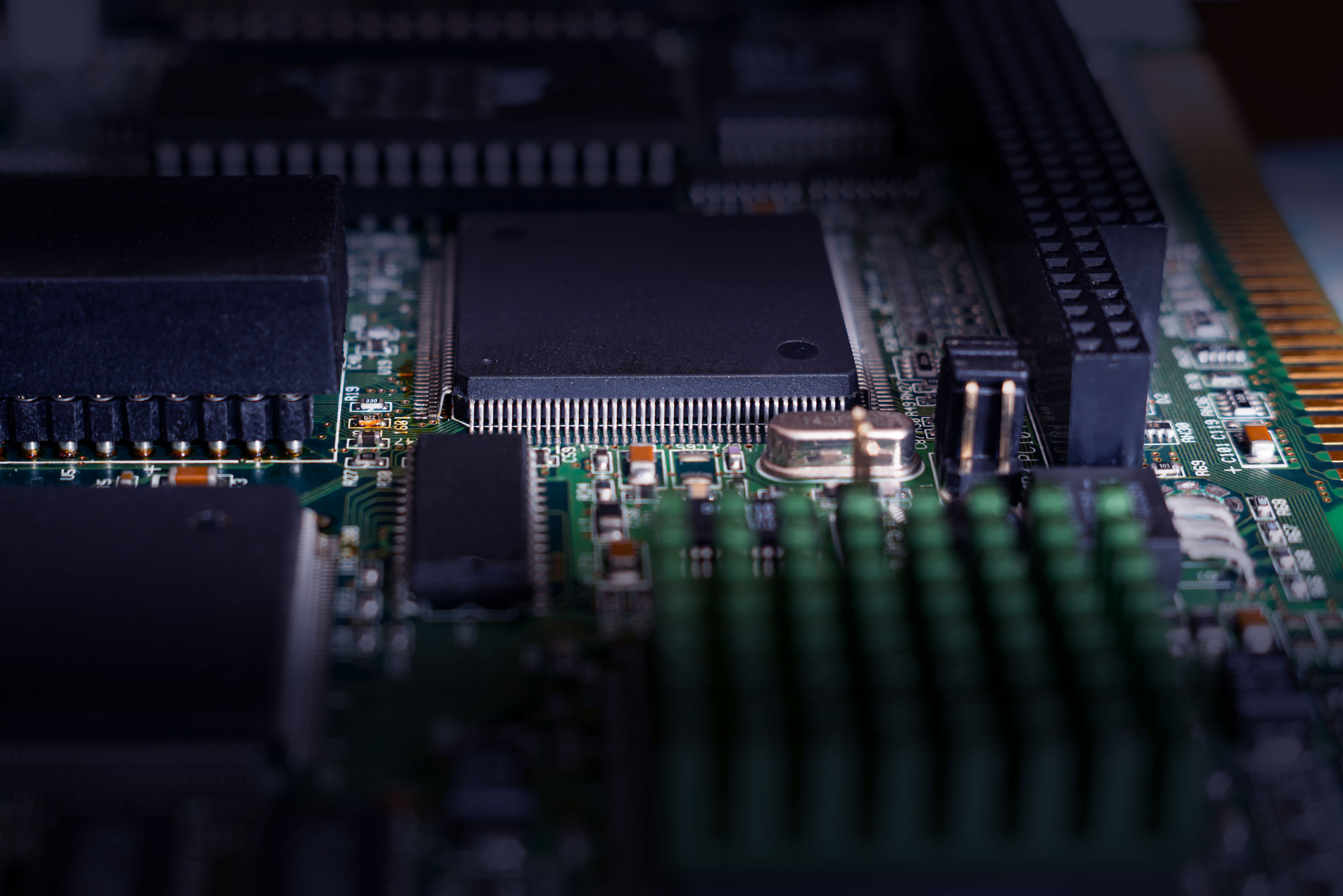
In the electronics industry, helium plays a crucial role in semiconductor manufacturing. Its inert nature helps create a controlled environment during the production process, protecting delicate components from contamination. Furthermore, helium's thermal properties are used in cooling systems to maintain the integrity of high-performance computing hardware.
Manufacturing processes also benefit from helium's properties. It is used in leak detection systems due to its small atomic size, which allows it to easily penetrate tiny cracks and fissures. This capability helps ensure product integrity by identifying flaws that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Medical and Healthcare Uses
Helium is integral to the healthcare industry, particularly in the functioning of MRI machines. These machines rely on superconducting magnets cooled by liquid helium to produce detailed images of the human body. The reliability and efficiency of helium as a coolant are critical to the performance of these life-saving devices.
Beyond MRI technology, helium is also used in respiratory treatments. Its low density makes it easier for patients with respiratory issues to inhale, improving airflow in conditions such as asthma and COPD. This therapeutic application underscores helium's versatility and importance in medicine.

Environmental and Safety Considerations
While helium is non-toxic and poses minimal environmental risks, it is a finite resource. Effective management and recycling are essential to ensure its availability for future industrial applications. Industries are adopting strategies to minimize waste and improve recovery processes.
Safety is another critical aspect when handling helium. Although generally safe, proper storage and handling procedures must be followed to prevent accidental leaks and ensure that equipment operates efficiently.

Future Prospects of Helium Use
The future of helium in industrial applications looks promising as technological advancements continue to expand its uses. Research into more sustainable extraction methods and better recycling techniques is ongoing, aiming to secure a steady supply of this valuable resource.
As industries strive for greater efficiency and innovation, helium will likely play an increasingly significant role. Its unmatched properties make it a cornerstone for developing cutting-edge technologies across various fields.

